Guest post!
Diabetes Mellitus, also known as diabetes, is quite a common disorder for humans and animals alike. When one has diabetes, they are unable to regulate their blood sugar levels because they lack insulin in their bodies.
Sugar in the blood results in the pancreas secreting insulin. Sugar is moved to the body cells where it is then used for energy, and it is the insulin’s job. Complications may happen without this energy.
There are two forms of diabetes:
-
Type 1 diabetes
Is that when a dog’s body does not produce insulin. This type is the most commonly found in dogs of various breeds.
-
Type 2 diabetes
Is that when a dog’s body does produce insulin and its body does not respond to it. This is also called “insulin resistance.”
Dogs diagnosed with diabetes mostly remain diabetic for the rest of their lives. Usually, they will need lifelong insulin injections, even if feeding and dietary adjustments are applied to keep their sugar levels low.
Additionally, the more advanced your dog’s stage gets, the more dangerous it will be for him or her. He may start to lose his appetite, and may eventually become lethargic.
Diabetes can also cause weakness and dehydration. In worst cases, the dog may slip into a comatose if not taken care of properly.
Diabetic dogs will also be at risk of receiving other health issues, not just diabetes.
Causes of diabetes in dogs
Just like people, there may be several causes why dogs get diabetes. Here are some of the most common ones:
-
Breed
Studies suggest that mixed breed dogs are more prone to diabetes. On the other hand, Golden Retrievers, Mini Schnauzers, Poodles, and German Shepherds, among many others, are known to be prone to having diabetes.
-
Age
It is quite unclear when dogs usually develop diabetes, but just like humans, they generally get it the older they get (at around ages 6 to 9).
-
Gender
Although both genders can get diabetes, females seem to be more prone.
-
Diet
Obesity does not necessarily cause diabetes, but it can make things harder for a diabetic dog. Therefore, dog diets should be watched carefully, making sure to have foods low in fat and carbohydrates.
Dietary tips for dogs with diabetes
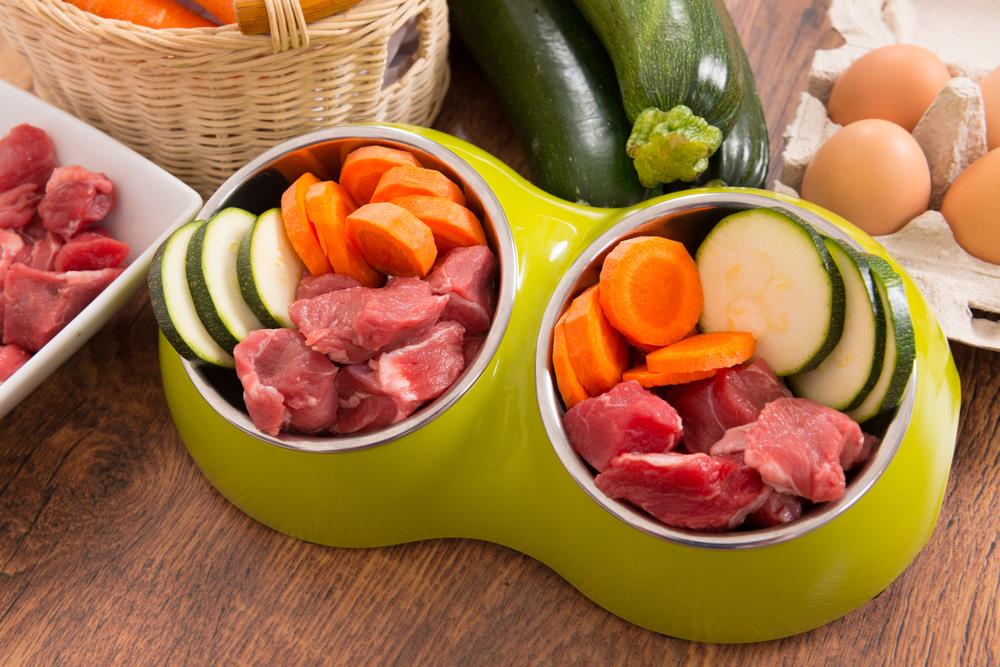
Meat-based and high-protein meals are most recommended for dogs with diabetes. Carbohydrates should remain low glycemic, too.
You should always remember to keep your dog’s food low in fat if your dog has pancreatitis or a high blood fat level. Furthermore, do not forget training hours for your dog using dog training collar.
Studies suggest that diets that are high or moderately high in fiber contents may be able to help minimize fluctuations in the blood sugar levels of dogs after eating. But, at other times, it may cause some weight loss, especially in thinner dogs.
To keep controlling your pet’s sugar levels, you can consider giving him or her a fixed meal at certain times of every day. After an hour of every meal, give your dog its insulin injection to battle possible rising sugar levels. Their meals should have the same amount of calories and the same ingredients to make sure the insulin works well.
Be careful when giving your dogs treats because these may cause blood sugar to rise, especially when given at random times of the day. As a result, the insulin may not control it well.
Although, 4-6 hours after an injection, it is safe to give the treats if you wish. Choose treats that are high in protein and avoid commercial treats as they may contain high sugar levels.
There are several dog foods for all types of dogs. Dog foods for Pitbulls, dog foods for puppies, likewise, there are dog foods for dogs with diabetes. Hence, here are some of the foods for dogs with diabetes:
Conclusion
Diabetic dogs can be helped with just commercial dog food, especially for their conditions. You just have to know what they need. Just make sure their food is high in protein and low in fat and carbohydrates.
You should also never forget to ask your veterinarian what dog food and other things your pet needs. After all, vets know best!
About Author:
DISCLAIMER: DogExpress does not endorse or take responsibility for the content in the guest post.

 DogExpress
DogExpress






















 in Chandigarh, India.
in Chandigarh, India. 
